Amazon Web Services (AWS) will invest $100 million in a program aiming to compete with Google and Microsoft in offering clients generative artificial intelligence (AI) access.
The Generative AI Innovation Center program will pilot and scale enterprise customers’ applications in generative AI.
Amazon Joins Big Investors Banking on AI
Amazon’s AI Program participants will benefit from free workshops and access Amazon Web Services’ code and text-generation tools CodeWhisperer and Bedrock.
The company will prioritize customers in finance, health, and life sciences and others previously expressing an interest in incorporating AI.
AWS trialed a 10-week AI startup program with its new Bedrock platform in April. Amazon trained Bedrock using both its own and third-party large-language models.
The project faltered as most customers reported they could not access the tool, with some clients claiming the company simply repackaged existing tools.
Portending well for Amazon’s AI program, however, is the onboarding of high-profile firms Stability AI and AI21.
Other notable firms recently investing in generative AI include Salesforce Ventures, a venture capital fund of Workday, and Dropbox. Over 3,000 AI startups received $52 billion in funding in 2022 alone.
AWS Investing Too Late?
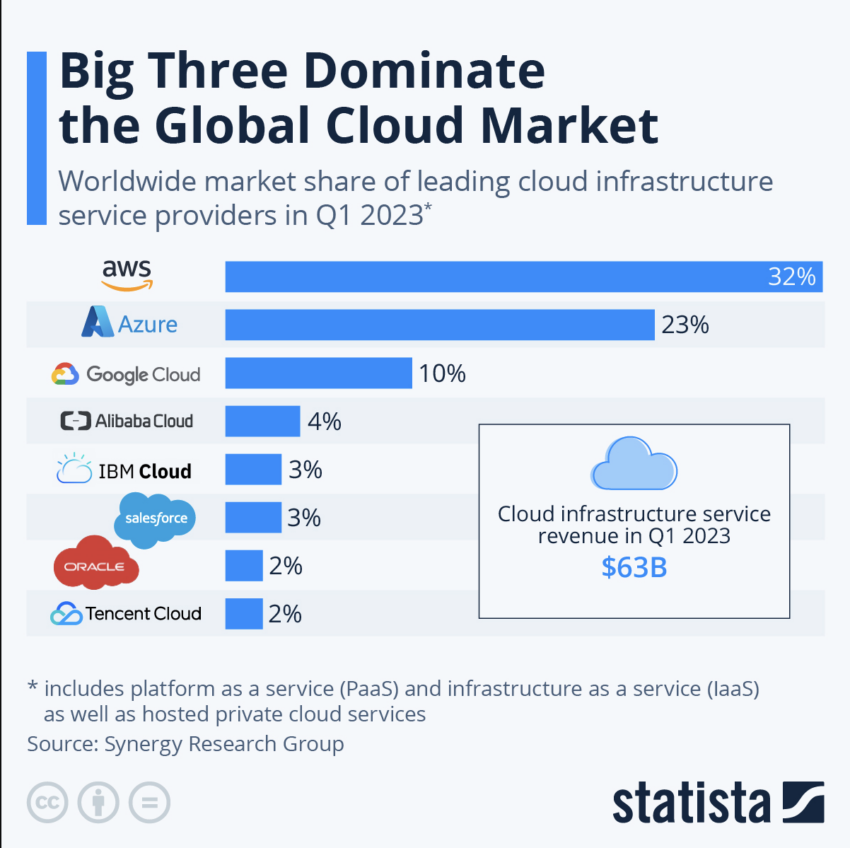
Amazon’s web division was the largest cloud provider globally in Q1 2023, followed by Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. However, AI could become the X-factor that drives future sales.
Google will open developer access to the Application Programming Interface for its revamped Bard assistant later this year. Bard can create computer code and can be integrated into medical applications.
Google parent Alphabet recently combined its DeepMind and Brain Research units to “significantly accelerate… progress in AI.”
For its part, Microsoft already supports ChatGPT, arguably the most popular conversational assistant. It recently incorporated its Bing search engine’s capabilities with the assistant.
OpenAI recently released its GPT-4 large language model without saying how much data it trained the tool on. Debates rage about whether companies can train models like GPT-4 on copyrighted data.
OpenAI boss Sam Altman recently lobbied Congress to create rules for AI before it becomes dangerous.
While industry players like Altman want regulators to limit AI’s threat to humanity, rights groups and politicians warn that AI is dangerous in its current form.
Its ability to convincingly cite fake information as true is challenging companies reliant on verified news to conduct business. False macro news, for example, can fool quant firms’ algorithms into trades that don’t make sense.
Earlier this year, a fake picture of an explosion at the Pentagon caused the S&P 500 to fall 0.3% in 30 minutes. Police later confirmed the image was a hoax.


 By
By
 By
By
 By
By
 By
By
 By
By